The Foundation of Digital Security
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) stands as a foundational element in the realm of digital security, providing a robust framework for managing cryptographic keys and securing communication. Understanding the intricacies of PKI is essential in comprehending its role in establishing trust and ensuring confidentiality in the digital landscape.
Key Components of PKI
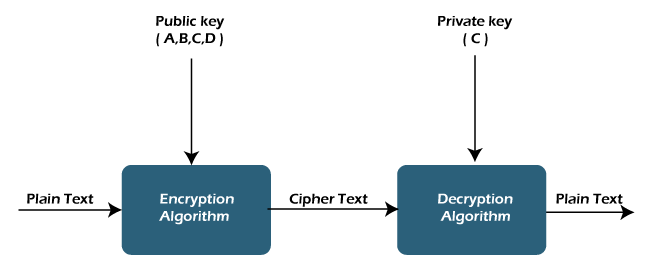
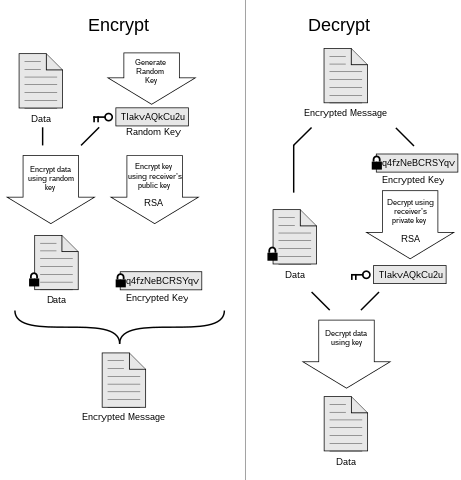
At the heart of PKI are cryptographic keys – public and private key pairs. These keys form the basis of secure communication. The public key, accessible to anyone, encrypts data, while the private key, known only to the key owner, decrypts the data. Certificates, issued by trusted entities called Certificate Authorities (CAs), link individuals or entities to their public keys, establishing a chain of trust within PKI.
Establishing Trust with Certificates
Certificates play a pivotal role in PKI by vouching for the authenticity of public keys. When a user receives a certificate from a trusted CA, they can rely on the associated public key as genuine. This process ensures that communication partners can trust each other’s identities, laying the groundwork for secure data exchange.
Encryption and Confidentiality
One of the primary purposes of PKI is to facilitate secure and confidential communication over untrusted networks, such as the internet. By encrypting data with public keys, only the corresponding private key holder can decrypt and access the information. This ensures that sensitive data remains confidential, even if intercepted during transmission.
Digital Signatures and Authentication
PKI enables the use of digital signatures, a crucial element in verifying the authenticity and integrity of digital messages. By signing a message with their private key, a sender provides a verifiable proof of authorship. Recipients can use the sender’s public key to authenticate the signature, ensuring that the message has not been tampered with.
PKI in Identity Management
Identity management is a key aspect of cybersecurity, and PKI plays a vital role in this domain. Through the issuance and validation of digital certificates, PKI contributes to secure user authentication and access control. This is particularly relevant in enterprise environments where managing user identities and permissions is critical.
PKI in E-commerce Transactions
In the world of e-commerce, where online transactions occur on a massive scale, PKI is instrumental in securing financial and personal information. The use of digital certificates ensures that users can trust the legitimacy of e-commerce websites and that their sensitive information is encrypted and protected during transactions.
Challenges and Solutions in PKI Implementation
While PKI offers robust security mechanisms, its implementation comes with challenges. Managing and securing private keys, dealing with certificate revocation, and ensuring the overall scalability of the infrastructure are areas that require careful consideration. Solutions involve proper key management practices, regular certificate validation, and the adoption of scalable PKI architectures.
Future Trends in PKI
As technology evolves, so does the landscape of cybersecurity. Future trends in PKI may involve advancements in quantum-resistant cryptography, decentralized identity management using blockchain technology, and improved automation for certificate lifecycle management. Staying abreast of these trends is crucial for organizations looking to maintain a resilient and future-proof PKI.
PKI: A Cornerstone of Cybersecurity
In conclusion, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) stands as a cornerstone in the field of cybersecurity, providing the necessary tools to establish trust, ensure confidentiality, and enable secure communication in the digital realm. Whether in identity management, e-commerce, or future technological advancements, the role of PKI remains pivotal in safeguarding our digital interactions.
To explore further into the world of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), visit PKI for additional resources and insights.