Exploring the Latest Advancements in Green Building Technology
Introduction to New Green Building Technology
In the realm of sustainable construction, new green building technology is continuously evolving, offering innovative solutions to enhance energy efficiency, minimize environmental impact, and improve occupant comfort. From cutting-edge materials to smart systems and design approaches, these advancements are reshaping the way buildings are designed, constructed, and operated, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable built environment.
Innovative Materials and Construction Techniques
One of the key areas driving the development of new green building technology is the use of innovative materials and construction techniques. Sustainable alternatives to traditional building materials, such as recycled steel, reclaimed wood, and engineered timber, are gaining popularity for their lower environmental footprint and superior performance. Additionally, advanced construction techniques, such as prefabrication and modular construction, streamline the building process, reduce waste, and minimize disruption to the surrounding environment.
Energy-Efficient Systems and Design Strategies
Energy efficiency is a central focus of new green building technology, with advancements in systems and design strategies aimed at reducing energy consumption and optimizing performance. High-performance building envelopes, energy-efficient HVAC systems, and smart lighting controls are just a few examples of technologies that improve energy efficiency while maintaining occupant comfort. Additionally, passive design strategies, such as orientation, shading, and natural ventilation, maximize the use of natural resources to further reduce energy demand.
Smart Building Automation and Controls
The integration of smart building automation and controls is revolutionizing how buildings are managed and operated. These systems leverage sensors, actuators, and data analytics to optimize energy use, enhance indoor air quality, and ensure optimal building performance. From automated lighting and HVAC controls to predictive maintenance and fault detection, smart building technologies empower building owners and operators to make data-driven decisions and maximize efficiency.
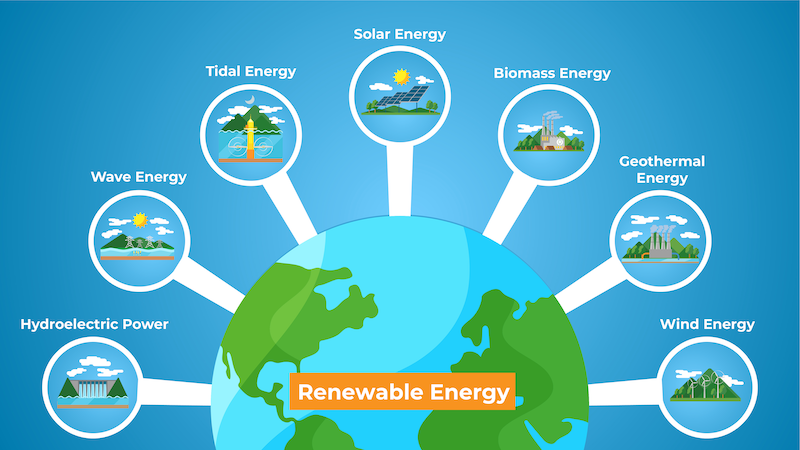
Renewable Energy Integration
Renewable energy integration plays a critical role in new green building technology, allowing buildings to generate clean energy onsite and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Solar photovoltaic panels, wind turbines, and geothermal heat pumps are among the renewable energy technologies commonly integrated into green buildings. By harnessing the power of the sun, wind, and earth, buildings can generate their own electricity and heat, contributing to a more sustainable energy future.
Water Conservation and Management
Water conservation and management are integral components of new green building technology, with a focus on reducing water consumption and minimizing wastewater generation. Low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and greywater recycling technologies help buildings conserve water resources and lower utility costs. Additionally, advanced irrigation systems and landscaping practices optimize outdoor water use and promote biodiversity, further enhancing sustainability.
Healthy Indoor Environments
Creating healthy indoor environments is another priority of new green building technology, with a focus on improving indoor air quality, thermal comfort, and acoustics. Low-emission building materials, such as paints, adhesives, and furnishings, minimize indoor air pollutants and enhance occupant health. Additionally, natural ventilation systems, daylighting strategies, and ergonomic design elements create spaces that are comfortable, productive, and conducive to well-being.
Resilient and Sustainable Design
Resilient and sustainable design principles are increasingly being incorporated into new green building technology, with a focus on enhancing building durability and adaptability to climate change. Flood-resistant construction, resilient building materials, and passive design strategies help buildings withstand extreme weather events and minimize damage. Additionally, green infrastructure, such as green roofs and permeable pavements, mitigate urban heat island effects and reduce stormwater runoff, enhancing overall sustainability.
Life Cycle Assessment and Environmental Impact
Life cycle assessment (LCA) and environmental impact analysis are essential tools used in new green building technology to evaluate the environmental performance of buildings over their entire life cycle. These analyses consider factors such as embodied energy, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource consumption to identify opportunities for improvement and inform design decisions. By quantifying environmental impacts, building professionals can make informed choices that minimize ecological footprints and maximize sustainability.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Collaboration and knowledge sharing are key drivers of innovation in new green building technology, with stakeholders across the building industry working together to exchange ideas, best practices, and lessons learned. Industry organizations, research institutions, and government agencies play pivotal roles in facilitating collaboration and advancing the state of the art in sustainable construction. By fostering a culture of innovation and continuous learning, the building industry can accelerate the adoption of new green building technology and create a more sustainable built environment.
Conclusion
New green building technology represents a paradigm shift in how buildings are designed, constructed, and operated, offering innovative solutions to address pressing environmental challenges. From innovative materials and energy-efficient systems to smart automation and renewable energy integration, these advancements are transforming the built environment and driving sustainability forward. By embracing new green building technology and prioritizing sustainability in all aspects of building design and construction, we can create healthier, more resilient, and more sustainable communities for generations to come.