Ensuring Security: Best Practices in Key Management
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity, secure key management stands as a crucial aspect of safeguarding sensitive information and protecting digital assets. This article explores the best practices in key management, emphasizing the importance of robust strategies to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of cryptographic keys.
The Foundation of Encryption: Key Management
Encryption is a cornerstone of cybersecurity, and its effectiveness relies heavily on secure key management. Cryptographic keys, whether for symmetric or asymmetric encryption, play a pivotal role in securing data. The strength of the encryption hinges on how well these keys are managed and protected.
Key Generation and Storage
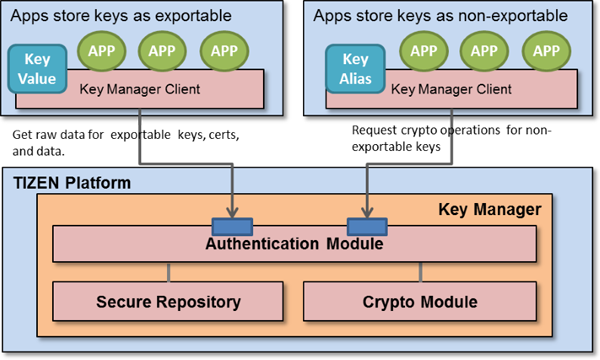
Secure key management begins with the generation of strong cryptographic keys. Employing reliable algorithms and ensuring randomness in the generation process are fundamental. Equally critical is secure storage. Keys should be stored in a manner that prevents unauthorized access, whether through encryption or hardware security modules (HSMs).
Lifecycle Management: Rotation and Revocation
Managing cryptographic keys throughout their lifecycle is essential. Regular key rotation reduces the risk associated with long-term key usage. Additionally, having mechanisms in place for key revocation is crucial in case a key is compromised. Properly handling key lifecycle events enhances overall security.
Access Control and Authentication
Restricting access to cryptographic keys is paramount. Implementing strong access controls ensures that only authorized individuals or systems can interact with the keys. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, reducing the risk of unauthorized key access.
Secure key management is vital for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of cryptographic keys. Explore additional insights and best practices on itcertswin.com.
Regular Audits and Monitoring
Continuous monitoring and periodic audits are essential components of key management. Monitoring ensures that any suspicious activities related to key usage are promptly detected and addressed. Regular audits help assess the overall effectiveness of the key management system.
Secure Transmission of Keys
The secure transmission of cryptographic keys is often a vulnerable point. Employing secure channels and protocols for key distribution is crucial. This ensures that keys reach their intended destinations without interception by malicious actors.
Disaster Recovery Planning
Contingency planning is a critical aspect of key management. Establishing robust disaster recovery plans ensures that cryptographic keys can be recovered in the event of hardware failures, natural disasters, or other unforeseen circumstances. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and potential data loss.
Training and Awareness
Human factors are often a weak link in cybersecurity. Training staff on the importance of secure key management, the risks associated with mishandling keys, and the implementation of best practices enhances the overall security posture of an organization.
Integration with Overall Security Strategy
Secure key management should be an integral part of the organization’s overall security strategy. Aligning key management practices with broader security initiatives ensures a holistic approach to protecting sensitive information and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Secure key management is a dynamic field that requires continuous adaptation to emerging threats. Stay informed about the latest developments and best practices to fortify your organization’s key management strategy. Explore additional resources on itcertswin.com for comprehensive insights into secure key management practices and cybersecurity.